Oncology is one of the most needed departments in medicine.
In the Oncology department, which deals with the formation of cancer, treatment begins after the diagnosis of the disease.



Oncology is a broad field of medicine that deals with the cause and treatment of cancer as well as its occurrence. Today, malignant tumors, which are on the rise, are called cancer. In Turkish, the term Oncology means “Cancerology”. Oncology requires serious knowledge and experience. Oncologists therefore work in collaboration with surgical specialists.

There are also areas of oncology. In addition to surgical oncology, there are also medical oncology and radiation oncology. In addition, radiation oncology, together with joint studies, the treatment and follow-up of cancer disease is also done correctly.

Cancer patients are followed up by medical oncology with drug treatment. Surgical oncology service ensures safe removal of cancerous tissue. Radiotherapy treatment is handled by the radiation oncology department.

Some doctors specialize in oncology. Doctors who specialize in oncology are called Oncologists. Medical oncologists always play an important role in a patient’s fight against cancer.
1
Oncologists conduct research and investigations into the formation and diagnosis of tumors in the body. Oncologists also play important roles in cancer treatment. Scientists who work on oncology are called oncologists. Oncologists also determine the structure of cancer by dealing with cancer and cancer derivatives. They also deal with the surgical operations of the cancer that is diagnosed and treated.
2
Oncologists specialize in cancerous cells. The field of Oncology, which has an important place in the medical world, deals with many diseases. In particular, Oncology Specialists deal with leukemia, kidney cancer, liver cancer, bone cancer and many other types of cancer. Oncology specialists start the treatment process after diagnosing the types of cancer that occur in the body.
3
Chemoterapy inhibits the growth of tumor cells. It also aims to destroy these cells. Chemotherapy drugs are determined by the type and size of the cancer. Some of these drugs are given orally and most are given intravenously. These chemotherapy drugs used to destroy cancer are very powerful. Some chemotherapy drugs are used to reduce the effects of tumor-fighting drugs.
Oncology, which has a wide scope, is divided into sub-branches.
Gynecologic Oncology: It is the branch that deals with the type of cancer that starts in the reproductive organs in women.
Medical Oncology: It is known as a field that specializes in chemotherapy drugs in cancer patients.
Pediatric Oncology: When cancer is diagnosed in children, this field deals with the diagnosis and treatment of cancer.
Radiation Oncology: Specializes in radiotherapy in the field of cancer.
Surgical Oncology: This is the field that deals with cancer-related biopsy and tumor removal. Oncology surgeries are also performed.
In the oncology department, the treatment process starts after cancer patients are diagnosed. The most important part of this treatment process, which is initiated by many doctors coming together, is known as the chemotherapy phase. During the chemotherapy phase, cancer is treated with medication. This treatment process is directed by a Medical Oncologist.
Posts
Screening Guidelines for Colon Cancer Explained
Colon cancer usually begins as small growths in the colon lining that may remain harmless for years before slowly changing into cancer over time. Screening aims to detect and remove[…]
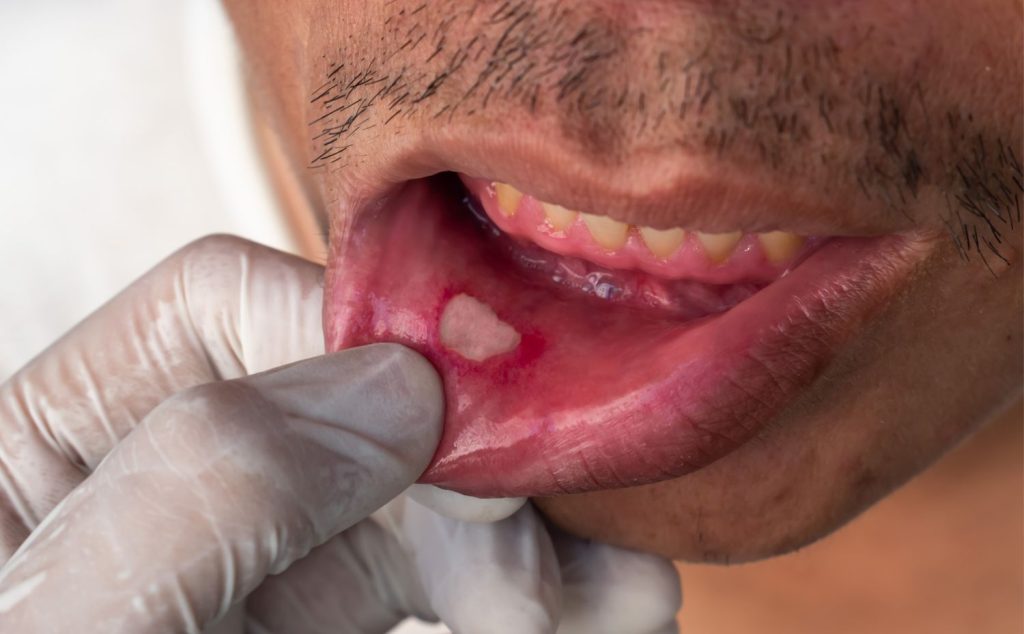
Read moreMouth Sores From Cancer Treatment: Relief Tips
Mouth sores during cancer therapy often catch patients off guard because they appear suddenly and disrupt basic routines. Eating becomes uncomfortable, speaking feels strained, and even swallowing can require extra[…]
Read moreCoping With Anxiety and Depression During Cancer
Have you ever noticed how one medical appointment can shake your entire sense of stability, even if the news isn’t as bad as you feared? Many patients describe this feeling[…]
Read moreThe Importance of Regular Cancer Screenings
Have you ever found yourself thinking you feel perfectly fine and therefore a medical check can wait? Many people delay screenings for that exact reason because the absence of symptoms[…]
Read moreHow to Navigate Life After Cancer Treatment
You hear the last infusion pump fall silent. The room looks familiar and strange. People smile while you count quiet questions. What happens to energy next week? When will routine[…]
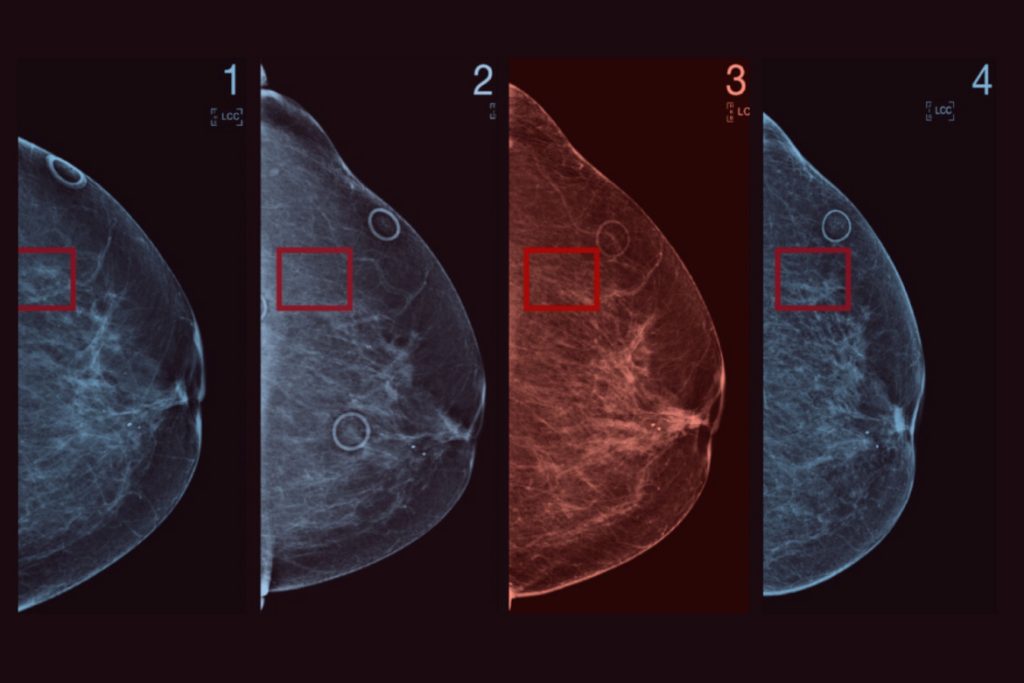
Read moreLatest Advances in Early Breast Cancer Detection
The ongoing effort to improve breast cancer detection involves a complex interplay of hardware innovations, computational refinement, and a deeper understanding of tissue biology, moving far beyond the simple two-dimensional[…]
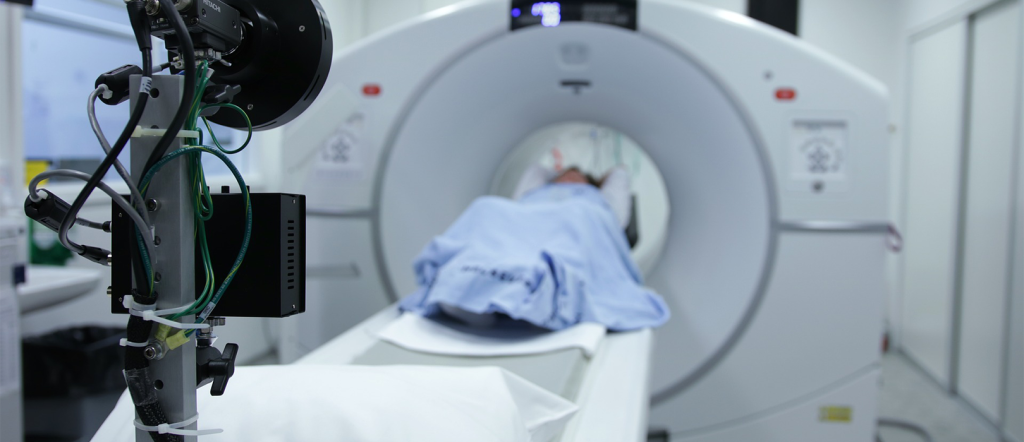
Read moreThe Role of PET Scans in Cancer Diagnosis
The integration of advanced molecular imaging techniques has fundamentally reshaped the landscape of oncological practice, moving the diagnostic and staging process beyond mere structural depiction to the realm of cellular[…]
Read moreHow to Support and Care for a Loved One With Cancer
The landscape of a cancer diagnosis changes everything, not just for the person facing the illness, but for every loved one orbiting their life. It is an immediate, seismic event[…]
Read moreThe Vital Role of Oncologic Surgeons in Cancer Treatment
The function of the oncologic surgeon in the modern context of cancer care is fundamentally misunderstood if viewed only as the specialist who excises the tumor. While the removal of[…]
Read more